Difference between revisions of "Guide to General Import and Export"
(→What else is there?) |
(→Variables definition) |
||
| (43 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
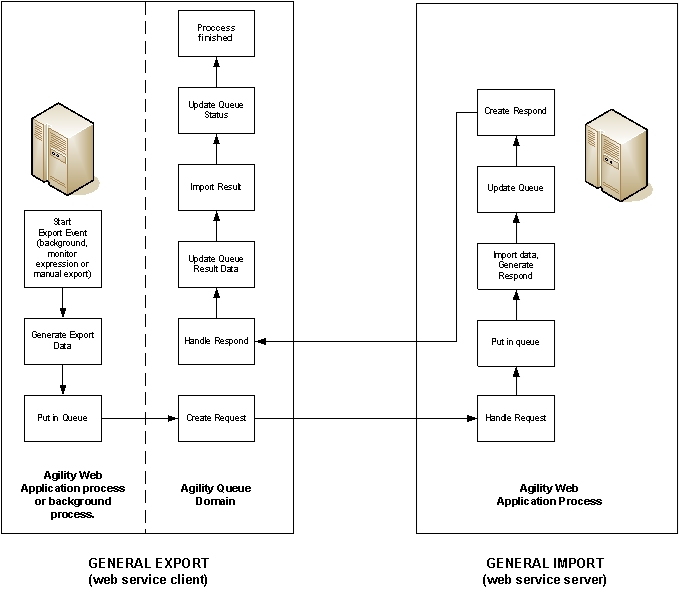
It is also possible to publish the Import definition as web service and the export definition as a web service client. This functionality allows distribution of Agility data to other systems | It is also possible to publish the Import definition as web service and the export definition as a web service client. This functionality allows distribution of Agility data to other systems | ||
[[File:obraz1.png]] | [[File:obraz1.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Before you start == | == Before you start == | ||
| Line 96: | Line 98: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
This ''header'' element is used to build proper request format and response headers when Export is used to communicate over http protocol. | This ''header'' element is used to build proper request format and response headers when Export is used to communicate over http protocol. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Configuration section also can have settings for controlling connection parameters and allow performing login process if required using separate request. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| + | <connection> | ||
| + | <url>/ISWorksOrders/ReadWorksOrders?Status=X</url> | ||
| + | <method>GET</method> | ||
| + | <login> | ||
| + | <exportcode>ContenderLogin</exportcode> | ||
| + | <sessionid>’Session id expression’</sessionid> | ||
| + | </login> | ||
| + | </connection> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The connection parameters define following features: | ||
| + | * <'''url'''> - Url defines suffix part of url which is connected with prefix part taken from Remote Connection object configured for that export. It enables to use single remote connection object for multiple request going to different service urls located on the same web server. This parameter may be suffixed by some additional value when “RequestParameters” global variable is defined and set within the the <contents> section of the export definition (see Section 2.2.5). | ||
| + | * <'''method'''> - overrides method HTTP connection for accessing remote web service | ||
| + | * <'''login'''> - login section defines login feature which performs separate request to login to the web service. The separate request is defined as export using the same Remote connection object. In result of that export the received cookies will be used by all request in the same session: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :::* <'''exportcode'''>- export definition code used to login to web service | ||
| + | :::* <'''sessionid'''> - string expression which result is session id code. It is optional but if used the separate logins will be done for every session id. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | When connection/login feature is used the additional request will be shown in import export queue. That export will be connection/login/exportcode export done when the login is required ( web service answers with 401 unauthorised code). | ||
==== Useful export string expression functions ==== | ==== Useful export string expression functions ==== | ||
| Line 166: | Line 192: | ||
</dbfilter> | </dbfilter> | ||
| − | + | <span style="background-color: Yellow"><variable> | |
<name>JobID</name> | <name>JobID</name> | ||
<value>woJob.JobID</value> | <value>woJob.JobID</value> | ||
| − | </variable> | + | </variable></span> |
... | ... | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 175: | Line 201: | ||
The Variable ''name'' is defined as a string and the ''value'' is defined as a string expression. | The Variable ''name'' is defined as a string and the ''value'' is defined as a string expression. | ||
In version 6.x introduced is shorter notation of variable: | In version 6.x introduced is shorter notation of variable: | ||
| − | <source lang ="xml"> | + | |
| − | + | <source lang ="xml"> | |
| + | <variable name="JobID">woJob.JobID</variable> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | |||
In version 5.1.12 introduced is new special variable called '''SKIPEXPORT'''. This variable is optionally and allows controlling output file generation process. When you want to use it, you have to add this variable in globally scope and set its value on '''true'''. The next in any other section like '''foreach''' you can set its value on '''false''' when any data to export exists. When variable is not set the system will be generated empty output file. | In version 5.1.12 introduced is new special variable called '''SKIPEXPORT'''. This variable is optionally and allows controlling output file generation process. When you want to use it, you have to add this variable in globally scope and set its value on '''true'''. The next in any other section like '''foreach''' you can set its value on '''false''' when any data to export exists. When variable is not set the system will be generated empty output file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Special Variables ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Special variable must be declared in Contents section. Variables declared in Contents section are visible outside export (to code which calls export). | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is special case of processing variables which are defined as global ( it measn defined outside foreach but possible changed in foreach key). All such variables are always populated to import definition included in export. It is used to transfer export context to result processing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | At the moment there are two special variables recognized by system: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # OnErrorMessage. When OnErrorMessage is not null then value of this variable will be written to export log in case of exception. | ||
| + | # RequestParameters. This variable is used to specify additional parameters which will be used in generating the url when the export is configured to be sent to the Web Service. | ||
| + | |||
| + | OnErrorMessage must be declared in contents section: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| + | <contents> | ||
| + | <variable> | ||
| + | <name>OnErrorMessage</name> | ||
| + | <value>NULL</value> | ||
| + | </variable> | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then it can be overwritten in other sections: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| + | <foreach table="inPurchaseOrder" datacontext="externaldataset" classname="DataBO.Inventory.PurchaseOrderBO"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <variable> | ||
| + | <name>OnErrorMessage</name> | ||
| + | <value>"PO:"+inPurchaseOrder.OrderNumber</value> | ||
| + | </variable> | ||
| + | .... | ||
| + | </source> | ||
=== Functional way of describing XML/HTML === | === Functional way of describing XML/HTML === | ||
| Line 252: | Line 315: | ||
* '''QueueProcessEnabled''': enables or disables queue sub process. | * '''QueueProcessEnabled''': enables or disables queue sub process. | ||
* '''HandleExportEvents''': enables or disables export on Event | * '''HandleExportEvents''': enables or disables export on Event | ||
| + | * '''AcceptAllCertifications''': accept self signed and any other untrusted certificates | ||
| + | * '''SecurityProtocol''': possible options are Auto (default), Ssl3, Tls | ||
| + | |||
''Import Export Queue and Export on event'' are described in separate chapters. | ''Import Export Queue and Export on event'' are described in separate chapters. | ||
| Line 390: | Line 456: | ||
* retrieve request result | * retrieve request result | ||
* import retrieved result. | * import retrieved result. | ||
| + | |||
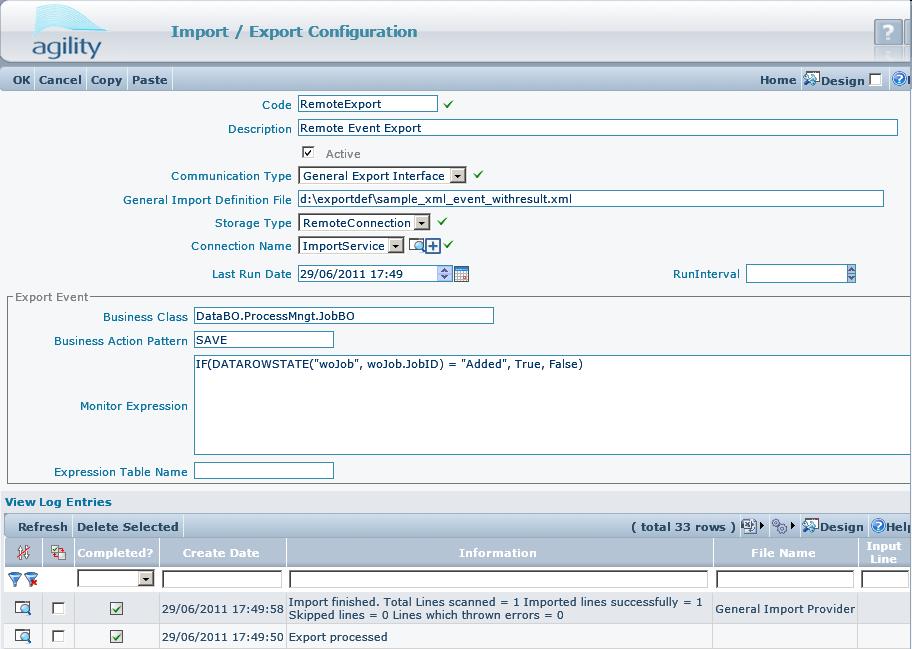
'''Remote Connection''' is an option for Storage Type of General Export. | '''Remote Connection''' is an option for Storage Type of General Export. | ||
| + | |||
[[File:obraz7.jpg]] | [[File:obraz7.jpg]] | ||
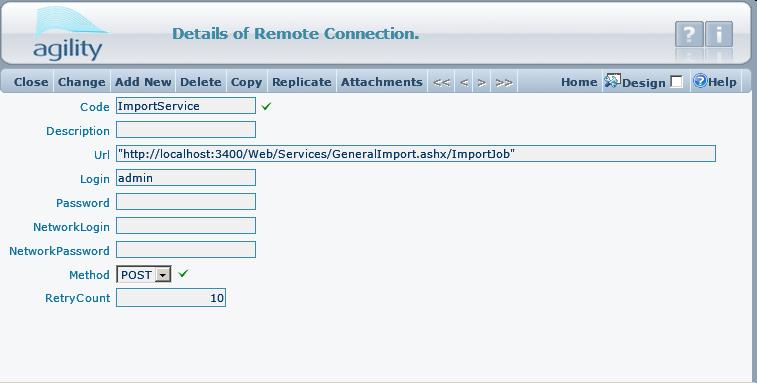
For Remote Connection You must define also ''Connection Name''. Connection describe link to host. | For Remote Connection You must define also ''Connection Name''. Connection describe link to host. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[File:obraz8.jpg]] | [[File:obraz8.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
* '''Url''': Host url. This is a string expression, which is evaluated just before create request to host. Some hosts may require putting login and password information inside the url. String expression will allow to do so: | * '''Url''': Host url. This is a string expression, which is evaluated just before create request to host. Some hosts may require putting login and password information inside the url. String expression will allow to do so: | ||
"http://somehost.org/Service?login=" + syImpExpRemoteConnection.Login | "http://somehost.org/Service?login=" + syImpExpRemoteConnection.Login | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Auth Type: Authentication type definition. Allowed values: | ||
| + | :::* '''Auto (also NULL)''' | ||
| + | :::If NetworkLogin is not specified then Agility will connect without credentials (authentication). If NetworkLogin is present then .NET will select appropriate Authentication Type according to remote service requirements. Possible Types are: Basic, Digest, NTLM, Negotiate. | ||
| + | :::* '''Windows''' | ||
| + | :::Uses windows integrated authentication. Used are credentials from user on which agility service is running. | ||
| + | :::* '''Digest''': Forces Digest auth. | ||
| + | :::* '''Basic''': Forces Basic auth. | ||
| + | :::* '''BasicNoChallenge''': Forces Basic auth with each request. This option should be used only when remote service is unable to work with "Challenge Pattern". '''Pre Authenticate''' should have no effect with this Auth type, but it is recommended that it is set to false. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Pre Authenticate''': It is boolean property which can be set to each request from agility to remote service. In general it controls if authentication credentials should be cached with subsequent requests. Unfortunately there is no clear explanation of behavior of this flag with different authentication types. Reversed Engineered Recommendation is to set this flag to '''true''' only with Digest or Basic auth. | ||
* '''Login and Password''': Helps to define internal web service credentials, you can put them in url and inside export body (will be explained further) | * '''Login and Password''': Helps to define internal web service credentials, you can put them in url and inside export body (will be explained further) | ||
| + | |||
* '''NetworkLogin and NetworkPassword''': Those parameters define credentials for web server authorization (BASIC, DIGEST,...). Available are all methods supported by asp.net framework. | * '''NetworkLogin and NetworkPassword''': Those parameters define credentials for web server authorization (BASIC, DIGEST,...). Available are all methods supported by asp.net framework. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * '''Domian''': Allow to explicitly specify domain. Usually when remote service authentication relay on Domain it has defined default domain. In such case Domain can be skipped. | |
| + | |||
| + | * '''Method''': Http method GET or POST | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Retry Count''': System will try RetryCount times to communicate with the host before giving up. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Retry Delay''': Sleep time between retries (in seconds) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Soap Fault Retry Count''': Number of system attempts to call remote service when service returns soap fault. It is used only when underlying respond import recognizes fault and throws validation error in mappings sections. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Soap Fault Retry Delay''': Sleep time between soap fault retries (in seconds). It is used only when underlying respond import recognizes fault and throws validation error in mappings sections. | ||
| + | |||
When export is set up as "Remote Connection" then extra information, are available inside the export definition. As already mentioned, information available in Remote Connection Details, can be used to create export data. Data from Remote Connection Details can be accessed through string expression variables (globally available in any part of the export): | When export is set up as "Remote Connection" then extra information, are available inside the export definition. As already mentioned, information available in Remote Connection Details, can be used to create export data. Data from Remote Connection Details can be accessed through string expression variables (globally available in any part of the export): | ||
| Line 444: | Line 540: | ||
There is no extra functionality which binds export data with import. Import is a separate process which has access only to the result generated by the web service. For example if You wish to export some jobs to a service, and after successful export update with information that the export is processed properly by service, then the Service result must carry information to identify the job to be updated with import data. Check examples for better understanding: -('export\sample_xml_event_withresult.xml' and 'import\import_wojob_def.xml'). | There is no extra functionality which binds export data with import. Import is a separate process which has access only to the result generated by the web service. For example if You wish to export some jobs to a service, and after successful export update with information that the export is processed properly by service, then the Service result must carry information to identify the job to be updated with import data. Check examples for better understanding: -('export\sample_xml_event_withresult.xml' and 'import\import_wojob_def.xml'). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Request Retry on Web exceptions ==== | ||
| + | |||
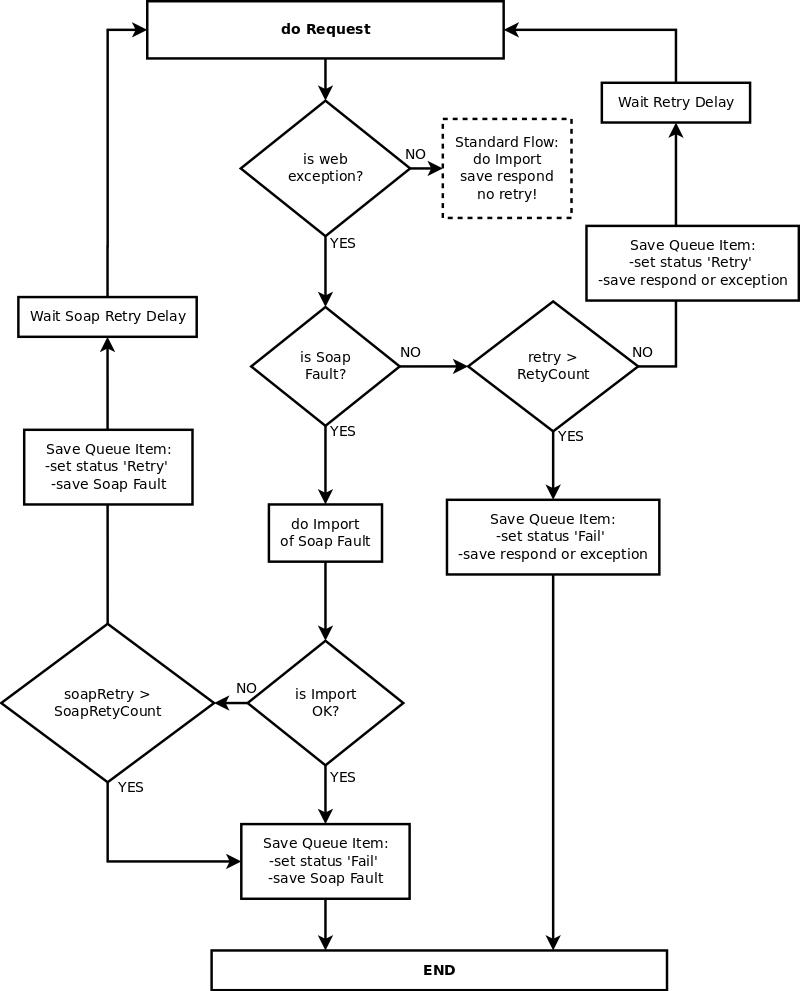
| + | When system do request to remote system it is possible that remote system is not available or return exception "Soap Fault". In both cases it is WebException. When remote service is unavailable then '''Retry Count''' and '''Retry Delay''' is used (Remote Connection Definition). When remote service respond with Soap Fault then GI will always try to import this Fault. Import definition of respond not necessary must be aware of SoapFault. When handling of SoapFault is not defined in import then import will finish without error but with information that nothing was imported. In queue this respond will be marked as 'Fail'. In above situation no retry will be made to remote system. In some cases some Soap Error Types should cause Request Retry. It is possible with import definition. When validation in mappings section throws exception and respond is SoapFault then such Request is Repeated according to '''Soap Retry Count''' and '''Soap Retry Delay''' (Remote Connection Definition). Below diagram is representing flow of handling respond when WebException occurs. Each time when system will try to retry request it will update queue with MessageResult and will set status to Retry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:nowy.jpg]] | ||
=== Export and Import Queue === | === Export and Import Queue === | ||
| Line 459: | Line 562: | ||
The General Import is extended with capabilities of working as web service. | The General Import is extended with capabilities of working as web service. | ||
| − | [[File:obraz10.jpg| | + | [[File:obraz10.jpg|center|thumb|x150px| General Import Feeding ]] |
=== Import definition extensions for web === | === Import definition extensions for web === | ||
| Line 474: | Line 577: | ||
#Result.IsImported : row import status flag | #Result.IsImported : row import status flag | ||
Thanks to extended data placed in mappings, string expression is executed in context of already created/updated data by import. In other words you can access data in string expression from mappings: ''#Import.JobDescription'' and from agility ''woJob.JobCode'' | Thanks to extended data placed in mappings, string expression is executed in context of already created/updated data by import. In other words you can access data in string expression from mappings: ''#Import.JobDescription'' and from agility ''woJob.JobCode'' | ||
| − | |||
=== Import configuration === | === Import configuration === | ||
| Line 488: | Line 590: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | * '''ImportWebServiceEnabled''': it is general switch for import web service functionality. | + | ::* '''ImportWebServiceEnabled''': it is general switch for import web service functionality. |
| − | * '''DefaultUser, DefaultUserPass''': default user credentials used when request doesn't have credentials defined (explained in next chapter). | + | ::* '''DefaultUser, DefaultUserPass''': default user credentials used when request doesn't have credentials defined (explained in next chapter). |
| − | * '''WebServiceLocation''': This url has minor meaning for import. It is used for publishing wsdl definition with proper default url of web service. | + | ::* '''WebServiceLocation''': This url has minor meaning for import. It is used for publishing '''wsdl''' definition with proper default url of web service. |
| + | ::* '''ADIntegration''': If set to true then user authorization is based on Agility Active Directory Integration Configuretion (include role based integration). | ||
=== Logging to system === | === Logging to system === | ||
| Line 565: | Line 668: | ||
* '''Queue and log.''' All request data and results are stored in ImportExportQueue: | * '''Queue and log.''' All request data and results are stored in ImportExportQueue: | ||
| − | System Confiquration - > Import Export -> Queue. Import log place doesn't change. It is available in import export definition form details. | + | System Confiquration - > Import Export -> Queue. |
| + | |||
| + | Import log place doesn't change. It is available in import export definition form details. | ||
== Exchange data with localization == | == Exchange data with localization == | ||
| Line 571: | Line 676: | ||
There is a potential problem with data exchange when import and export works on machines with different cultures. By default all conversions are made with culture of running application. |The only safe way to get a portable format is to operate on invariant cultures. There are already capabilities embedded into string expression functions which allow conversion of data from and to an invariant culture. | There is a potential problem with data exchange when import and export works on machines with different cultures. By default all conversions are made with culture of running application. |The only safe way to get a portable format is to operate on invariant cultures. There are already capabilities embedded into string expression functions which allow conversion of data from and to an invariant culture. | ||
<source> | <source> | ||
| − | + | ToInvariantStr(value) | |
| − | FromInvariantStr(type, value) | + | FromInvariantStr(type, value) |
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 578: | Line 683: | ||
There is additional convert function which is capable to convert data in desired culture. It can be used as replacement for ''ToInvariantStr, FromInvariantStr'' functions. | There is additional convert function which is capable to convert data in desired culture. It can be used as replacement for ''ToInvariantStr, FromInvariantStr'' functions. | ||
<source> | <source> | ||
| − | + | Convert(type, value, culture) </source> | |
''Type'' is a string with desired destination type ["decimal", "string", "int", datetime"]. | ''Type'' is a string with desired destination type ["decimal", "string", "int", datetime"]. | ||
| Line 591: | Line 696: | ||
Examples: | Examples: | ||
<source> | <source> | ||
| − | + | ToInvarintStr(inItem.price) | |
FromInvariantStr("decimal", #Import.price) | FromInvariantStr("decimal", #Import.price) | ||
| − | Convert("decimal", #Import.price, "en-GB") | + | Convert("decimal", #Import.price, "en-GB") |
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | |||
== New Features (Version7.1) == | == New Features (Version7.1) == | ||
| − | === String expression templates == | + | === String expression templates === |
Templates add-on for string expressions is mechanism which allows to create XML and HTML documents in more natural way. Quick example: | Templates add-on for string expressions is mechanism which allows to create XML and HTML documents in more natural way. Quick example: | ||
| Line 644: | Line 748: | ||
Currently there are defined three types of templates: | Currently there are defined three types of templates: | ||
# template-raw ["Area " + 3*4 + " square metres"] | # template-raw ["Area " + 3*4 + " square metres"] | ||
| − | + | # template-html ["Area " + HtmlEncode(3*4) + " square metres"] | |
| − | + | # template-xml ["Area " + XmlEncode(3*4) + " square metres"] | |
| − | + | # stringexpression | |
Only difference with templates raw/html/xml is encoding of string expression result. Raw does not encode string expression. When type is set to “stringexpression” then template engine is not used and standard string expression must be used. | Only difference with templates raw/html/xml is encoding of string expression result. Raw does not encode string expression. When type is set to “stringexpression” then template engine is not used and standard string expression must be used. | ||
| Line 652: | Line 756: | ||
In export template is declared in type attribute: | In export template is declared in type attribute: | ||
<source> | <source> | ||
| − | <data | + | <data type="template-xml">... |
| − | <const | + | <const type="template-xml">... |
| − | <variable | + | <variable type="template-xml">... |
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | |||
By default templates are not used but it is possible to set default template for whole export definition. When attribute ''defaulttype'' is set in contents element then all string expression elements will use default template without need to specify type in each element. Even if ''defaulttype'' attribute is set it is possible to override particular section with other template type. | By default templates are not used but it is possible to set default template for whole export definition. When attribute ''defaulttype'' is set in contents element then all string expression elements will use default template without need to specify type in each element. Even if ''defaulttype'' attribute is set it is possible to override particular section with other template type. | ||
| + | |||
<source> | <source> | ||
| − | <export><contents | + | <export><contents defaulttype="template-html">... |
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 740: | Line 846: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Partial structure is created and evaluated during export runtime with ''include'' macro or function. Partial will inherit parent context. It means that the same partial evaluation depends on context it is executed. It also means that partial not require full context definition (''classname, datacontext'') as it is inherited from caller. | Partial structure is created and evaluated during export runtime with ''include'' macro or function. Partial will inherit parent context. It means that the same partial evaluation depends on context it is executed. It also means that partial not require full context definition (''classname, datacontext'') as it is inherited from caller. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === <big>Import</big> === | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* [[import_wojob_def]] | ||
| + | :* [[MKC_Request_def]] | ||
| + | ==== In ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :::* [[import_wojob_sample]] | ||
| + | :::* [[MKC_Request_data_sample]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Out ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :::* [[MKC_Respond_sample]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === <big>Export</big> === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :* [[AttendeeAvailabilityExchangeEvents]] | ||
| + | :* [[BookingsAllEvents]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_csv]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_html]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_xml]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_xml_dataset_mode]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_xml_event]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_xml_event_withresult]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_xml_event_withresult_and_global_vars]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_xml_functional]] | ||
| + | :* [[sample_xml_scanexport]] | ||
| + | :* [[templates_mobilemainmenuexport]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Out ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :::* <source>file:///C:/Users/Aleksandra/Desktop/Dokumentacja%20-%20praca/examples/export/out/export.html]</source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :::* [[export_xls]] | ||
| + | :::* [[export]] | ||
| + | :::* [[export_dataset_mode]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:34, 5 July 2017
Contents
- 1 GIAE functionality overview
- 1.1 Before you start
- 1.2 General Export
- 1.2.1 Simple export example
- 1.2.2 The Export Definition
- 1.2.3 Functional way of describing XML/HTML
- 1.2.4 Generating JSON output
- 1.2.5 Export confinguration options can be found under 'configuration/interface' section:
- 1.2.6 Export Data to Pipe from scan
- 1.2.7 Export on Event
- 1.2.8 Export to Remote Connection
- 1.2.9 Export and Import Queue
- 1.3 General Import
- 1.4 Exchange data with localization
- 1.5 New Features (Version7.1)
- 1.6 Examples
GIAE functionality overview
This functionality allows export of data from agility to any text based file format (xml, comma separated value, html etc.). The export and import procedures can be run at defined intervals from the background process or manually. Additionally the export function can be defined as a monitor expression that will execute based upon a condition.
It is also possible to publish the Import definition as web service and the export definition as a web service client. This functionality allows distribution of Agility data to other systems
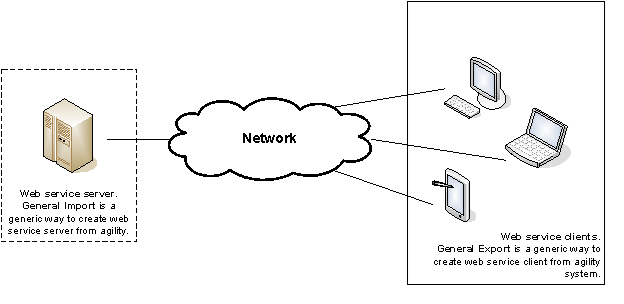
Before you start
General Import and Export operates with web services at a very low level. In other words to exchange data you must understand SOAP protocol structure using properly setup http headers.
It is recommended that a ‘RequestTool’ is available for design, configuration and testing.
A Request tool is an application which will help process the test procedure. This tool helps to generate http request, and grabs the request result.
A Request Tool has been included in Agility and is available under the default Agility Admin menu:
System Configuration -> Import Export -> Request Tool
General Export
Simple export example
You can think of and export definition as a sequential program written inside an xml file.
This Simple example showing a CSV export work order data where the work order start date is within the last 6 months will help to understand how it works.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<export>
<contents>
<const>
"JobCode" + Separator() + "Desc" + Separator() + "StartDate"+ Separator() + "Due" + NewLine()
</const>
<foreach table="woJob" datacontext="database" classname="DataBO.ProcessMngt.JobBO">
<dbfilter>
woJob.StartDate >= DATEADD(NOW(), 'MONTH', -6) order by woJob.StartDate
</dbfilter>
<data>
CsvEncode( JobCode, FullDescription, StartDate, DueDate ) + NewLine()
</data>
</foreach>
</contents>
</export>The ‘Const’ and ‘data’ sections hold string expressions which will be output to file after processing. The difference in those sections is only logical. The Const section is evaluated without context and is simply output ‘as is’, and the data is evaluated in the context of the foreach element. The key to understanding export is to understanding the foreach element.
This element is responsible for:
- the context and format of data to export
- filter and retrieve data to export
- loop through retrieved data results and:
- evaluate defined variables
- evaluate string expressions from all data sections defined inside foreach element,
- execute nested foreach elements
The Foreach element can operate on different datacontext instances, all the available options will be explained in next chapter. In above example datacontext is set to database. The database context requires additional parameters: table, classname, and dbfilter.
As you would expect in this context the system will create a query based on the definition in the dbfilter element. The Foreach element will then loop through results of the query contained in the dbfilter element and for each row the system will execute the string expression inside data element and will output to file. The String expression contains a few new functions which will help to produce well formatted xml or csv files.
This is a sample of the output from the above example
The Export Definition
Configuration section
The configuration section contains some parameters relating to formatting and behavior of the output
<export>
<configuration>
<separator>;</separator>
<textquote>"</textquote>
<newline>\n</newline>
<encoding>UTF8</encoding>
<header></header>
</configuration>
<contents>
...The above configuration sample show the default values of the configuration elements. The element names are self-explanatory with the exception of the header element which is explained below.
<export>
<configuration>
<newline>\n</newline>
<encoding>UTF8</encoding>
<header>
Content-Type: text/xml;
SOAPAction: http://www.fastnetasp.com/GeneralImport;
</header>
</configuration>This header element is used to build proper request format and response headers when Export is used to communicate over http protocol.
Configuration section also can have settings for controlling connection parameters and allow performing login process if required using separate request.
<connection>
<url>/ISWorksOrders/ReadWorksOrders?Status=X</url>
<method>GET</method>
<login>
<exportcode>ContenderLogin</exportcode>
<sessionid>’Session id expression’</sessionid>
</login>
</connection>The connection parameters define following features:
- <url> - Url defines suffix part of url which is connected with prefix part taken from Remote Connection object configured for that export. It enables to use single remote connection object for multiple request going to different service urls located on the same web server. This parameter may be suffixed by some additional value when “RequestParameters” global variable is defined and set within the the <contents> section of the export definition (see Section 2.2.5).
- <method> - overrides method HTTP connection for accessing remote web service
- <login> - login section defines login feature which performs separate request to login to the web service. The separate request is defined as export using the same Remote connection object. In result of that export the received cookies will be used by all request in the same session:
- <exportcode>- export definition code used to login to web service
- <sessionid> - string expression which result is session id code. It is optional but if used the separate logins will be done for every session id.
When connection/login feature is used the additional request will be shown in import export queue. That export will be connection/login/exportcode export done when the login is required ( web service answers with 401 unauthorised code).
Useful export string expression functions
- Separator() - Returns separator defined in configuration
- TextQuote() - Returns text quote defined in configuration
- NewLine() - Returns new line defined in configuration
- CsvEncode(arg1, arg2, ...) - Encode passed arguments to valid csv structure
- XmlEncode(arg) - Encode argument to valid xml text
- HtmlEncode(arg) - Encode argument to valid html text
- Convert(type, value, specific culture) – This converts values with optional culture specifications. Refer to section "Exchange data localization" for further information.
Classname property definition
Classname defines business object which will be used in child elements. Classname property can be used in foreach & contents elements.
<foreach table="woJob" datacontext="dataset" classname="DataBO.ProcessMngt.JobBO">In above example export will create new JobBO. Export functionality allows to pass "external" business object into export (from export control or when export is triggered on event). When some part of definition should operate on external business object then clasname should be prefixed with "External:"
<foreach table="woJob" datacontext="dataset" classname="External:DataBO.ProcessMngt.JobBO">External prefix is new functionality introduced in agility v6.x. Intention of this functionality is to replace and clarify external context understanding. From version 6 and above datacontext: externaldataset is obstolete. Instead "External:" prefix should be used in classname property.
Contents element similar like foreach can define classname too. In this case business object is used in evaluation of string expression functions (which is required for some functions like "SYSPARAM").
Foreach element definition
The foreach can operate on different datacontexts:
- dataset
The Business object declared in classname, fills the dataset by executing getDataByFilter (dbfilter). Extremely useful when you wish to export the whole business object data. Consideration should be given to filtering in the sense of using a wide filter as this can consume a lot of resource where a large row count is returned. The foreach elements can be nested. With nested foreach you can process child tables. Nested foreach can also skip context definitions (apart from the table property), in which case nested foreach will inherit context from its parent.
- externaldataset
Used in conjunction with "MonitorExpression". The Dataset for export is taken from the Business Object which fires MonitorExpression.
- database
This context creates a query based upon dbfilter and retrieves data using the declared business classname.
- externalselectedkeys
This context works similar to the database context. It adds to dbfilter keys selected from a scan to export or keys evaluated to true with MonitorExpression.
- query
This allows definition of a raw SQL query defined as queryfilter. For this to work table and database properties must be defined.
- mappings
This is used when the Export is embedded inside and Import to generate an "import result".
- expression
This context allows to retrieve rows directly from business object. It means that function which will feed export should be hardcoded into business object. Expression context should be avoided! It constrains export definition with hardcoded business logic. It should be used only when there is no other way to retrieve data. Please check "AttendeeAvailabilityExchangeEvents.xml" sample definition for usage details.
It is important to know that if the classname property is omitted then the context is inherited from the parent foreach element. If the classname property exists then system will always initialize a new business object (there is only one exception for this rule with externaldataset context).
The best way to understand how it works is to look at examples for the foreach element. The foreach element has many useful features;
- Infinite depth for nested foreach elements.
- A nested foreach can have its own context of any type (you can start with a dataset context and inside put a foreach with query context.)
- With the string expression you can grab any parent data by creating query’s on the fly. You can use this feature in all context types! Even if you create custom sql query (although in this case you must additionally define classname and table which must exist inside the specified business object dataset).
- Data can be filtered by the string expression. These string expressions should be defined inside a filter element, shown below:
<filter datarowstate= "Added,Modified,Deleted,Unchanged"> if(code="a1"; True; False)</filter>Variables definition
Variables can be defined directly inside export contents, and inside foreach elements as shown in the example below:
<foreach table="woJob" datacontext="database" classname="DataBO.ProcessMngt.JobBO">
<dbfilter>woJob.StartDate >= DATEADD(NOW(), 'MONTH', -6) order by woJob.StartDate
</dbfilter>
<span style="background-color: Yellow"><variable>
<name>JobID</name>
<value>woJob.JobID</value>
</variable></span>
...The Variable name is defined as a string and the value is defined as a string expression. In version 6.x introduced is shorter notation of variable:
<variable name="JobID">woJob.JobID</variable>In version 5.1.12 introduced is new special variable called SKIPEXPORT. This variable is optionally and allows controlling output file generation process. When you want to use it, you have to add this variable in globally scope and set its value on true. The next in any other section like foreach you can set its value on false when any data to export exists. When variable is not set the system will be generated empty output file.
Special Variables
Special variable must be declared in Contents section. Variables declared in Contents section are visible outside export (to code which calls export).
There is special case of processing variables which are defined as global ( it measn defined outside foreach but possible changed in foreach key). All such variables are always populated to import definition included in export. It is used to transfer export context to result processing.
At the moment there are two special variables recognized by system:
- OnErrorMessage. When OnErrorMessage is not null then value of this variable will be written to export log in case of exception.
- RequestParameters. This variable is used to specify additional parameters which will be used in generating the url when the export is configured to be sent to the Web Service.
OnErrorMessage must be declared in contents section:
<contents>
<variable>
<name>OnErrorMessage</name>
<value>NULL</value>
</variable>
....Then it can be overwritten in other sections:
<foreach table="inPurchaseOrder" datacontext="externaldataset" classname="DataBO.Inventory.PurchaseOrderBO">
<variable>
<name>OnErrorMessage</name>
<value>"PO:"+inPurchaseOrder.OrderNumber</value>
</variable>
....Functional way of describing XML/HTML
Along with linq microsoft introduced very flexible way of generating xml files using functions. Major part of this functionality is integrated in string expression. Idea is very simple. Xml document is created by set of functions which represent document. Functions available in string expressions: XDocument(object[]) XElement(name, object[]) XAttribute(name, object[]) XNamespace(url) Xmlns()
Please refer sample_xml_functional.xml for example definition. In time of writing it is not sure if functional description of xml document is better than outputting string directly in CDATA sections. Benefit of functional approach is that it guarantee valid xml structure and is resistant for "typo" bugs.
Generating JSON output
JSON is often used with ajax enabled web controls. It is commonly used for exchanging data with javascript as data written in JSON format do not require any transformation on javascript side.
Calendar event example in JSON format:
[
{
"id": 111,
"title": "Event1",
"start": "2013-12-10"
},
{
"id", 222,
"title": "Event2",
"start": "2013-12-20",
"end": "2013-12-22"
}
]Brackets [] are sequence notation and {} brackets are objects. All in all we have defined 2 objects in array. It is easy for export to generate such data format, but created are additional functions which makes it even simpler. There are two additional functions available in export (and in string expression).
JSequence and JObject. Above sample with usage of JSequence and JObject functions in string expression notation:
JSequence(
JObject(
"id", 111,
"title", "Event1",
"start","2013-12-10"
),
JObject(
"id", 222,
"title", "Event2",
"start", "2013-12-20",
"end", "2013-12-22"
)
)Benefit of using functional version is that it automatically handle data types conversion and will guard proper, comma, quotes, brackets notation.
It is good to know that with "functional way" each call function call is not immediately transformed to string, but created is structure which can be appended in any part of export and finally converted to string at end of export.
Please refer BookingsAllEvents.xml definition for example which is using JSON generator.
Export confinguration options can be found under 'configuration/interface' section:
<GeneralExport
QueueProcessEnabled="true"
HandleExportEvents="true"
/>- QueueProcessEnabled: enables or disables queue sub process.
- HandleExportEvents: enables or disables export on Event
- AcceptAllCertifications: accept self signed and any other untrusted certificates
- SecurityProtocol: possible options are Auto (default), Ssl3, Tls
Import Export Queue and Export on event are described in separate chapters.
The export shares a few options with the General Interface. The ImportExportQueue works in the same application domain as General Interface.
<GeneralWebService
RemoveLogAfterDays="1"
RemoveAllLogAfterDays="5"
userName="admin"
userPass="***"
/>userName and userPass define user on which queue app domain will work. This app domain is common for ImportExportQueue, GeneralInterface, and Receiver. The system will delete processed syImpExpQueue elements if they are older than value of RemoveLogAfterDays.
The system will delete any queue items (with any status) if they are older than RemoveAllLogAfterDays.
A ‘Cleanups’ check is running within queue appdomain (in the background): on application start, and periodically for each RemoveLogAfterDays.
Export Data to Pipe from scan
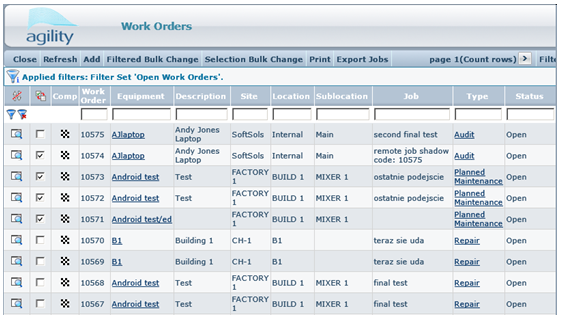
It can be seen that export is extremely flexible. Export can be used to create customized exports, accessible from scan forms. There are dedicated datacontext settings for the above scenario called: externalselectedkeys.
Below is an example export definition which can be attached to woJob scan to demonstrate this function.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<export>
<configuration>
<header>Content-Type: text/xml</header>
</configuration>
<contents>
<const>
<![CDATA[
"<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<JobList>
"
]]>
</const>
<foreach table="woJob" datacontext="externalselectedkeys" classname="DataBO.ProcessMngt.JobBO">
<dbfilter>order by woJob.JobCode</dbfilter>
<variable>
<name>JobID</name>
<value>woJob.JobID</value>
</variable>
<data>
<![CDATA[
"<woJob>
<Credentials>
<Login>" + XmlEncode(#RemoteConnection.Login) + "</Login>
<Url>" + XmlEncode(#RemoteConnection.Url) + "</Url>
</Credentials>
<JobCode>" + XmlEncode(JobCode) + "</JobCode>
<Description>" + XmlEncode(FullDescription) + "</Description>
<JobStatus>" + XmlEncode(syJobStatus.Description) + "</JobStatus>
<JobType>" + XmlEncode(syJobType.Description) + "</JobType>
<StartDate>" + XmlEncode(StartDate) + "</StartDate>
<DueDate>" + XmlEncode(DueDate) + "</DueDate>
"
]]>
</data>
<foreach table="woJobTask" datacontext="database" classname="DataBO.ProcessMngt.JobBO" >
<dbfilter>woJobTask.JobID = #JobID</dbfilter>
<filter>if(Code = 'Completed', false, true)</filter>
<data>
<![CDATA[
" <woJobTask>
<TaskCode>" + XmlEncode(Code) + "</TaskCode>
<Description>" + XmlEncode(Description) + "</Description>
<TaskType>" + XmlEncode(syTaskType.Code) + "</TaskType>
<TaskStatus>" + XmlEncode(syJobStatus.Description) + "</TaskStatus>
</woJobTask>
"
]]>
</data>
</foreach>
<data>
<![CDATA[
"</woJob>
"
]]>
</data>
</foreach>
<const>
<![CDATA[
"</JobList>
"
]]>
</const>
</contents>
</export>Externalselectedkeys context will export only records selected on the scan form;
Remember that you are not forced to use above context when exporting from scan this is just an example. Export can also be configured to ignore selected keys in a scan, the control is up to the export designer.
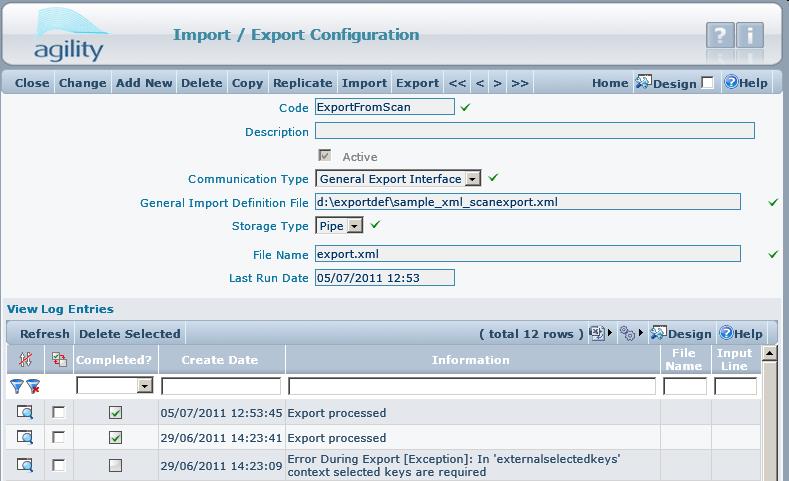
In export configuration the Storage Type should be set to Pipe. When storage type is set to pipe then the exported data is immediately send to the client web browser. It is possible to set different storage types, but then export will be run silently, and results will be passed to the selected Storage Type.
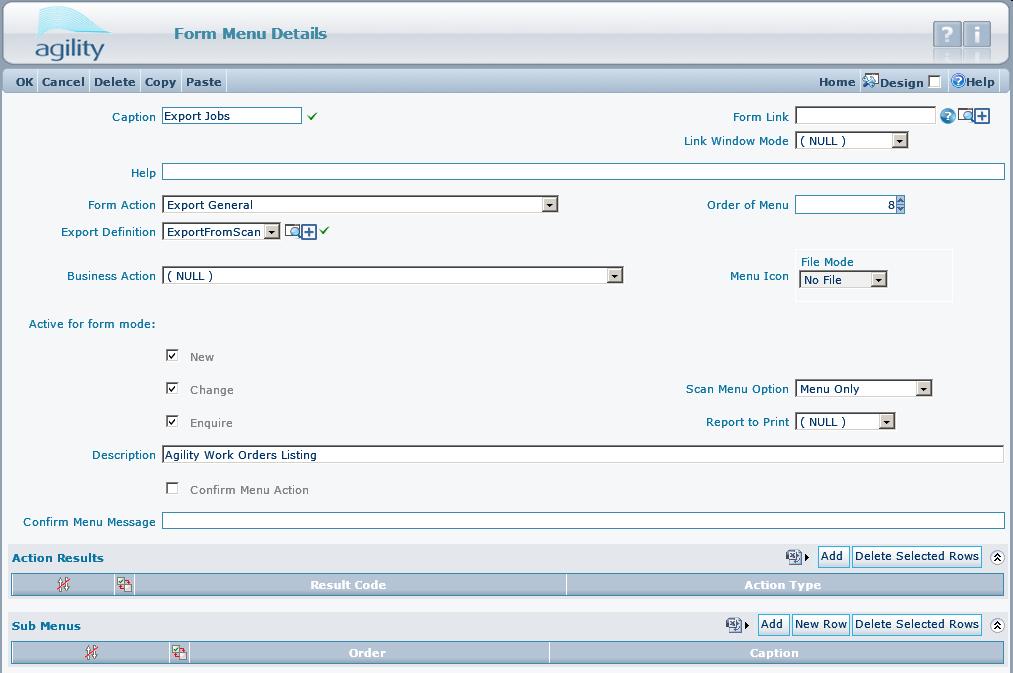
The export definition is attached to the scan form through the "form menu". Create a form menu item with the form action "Export General", and select the appropriate export definition from combo box.
In the above example, the export will generate an xml file. An simple example can be seen by attaching to the work orders scan, the export definition from examples directory called "sample_html.xml". As You can see export can be used to generate customizable html reports.
Export on Event
The system can run exports automatically, during the processing of some business actions. Data is exported when the string expression condition (defined in the export configuration) is evaluated to True.
Export on Event definition is exactly the same as system notification definition.
- Business Class: Define Business Object on with condition will be checked.
- Business Action Pattern: is the name of a business action which will run condition checks. When the pattern is equal to "ANY" then any business action executed with the defined business object will check conditions.
- Monitor Expression: Is a string expression. When evaluated to true then exports will be processed.
- Expression Table Name: By default, the main table of the business object. This must be a table which belongs to business object's data set. If you select a child table then the expression will be evaluated for each child row. When one or more rows are evaluated to true then the export will be executed.
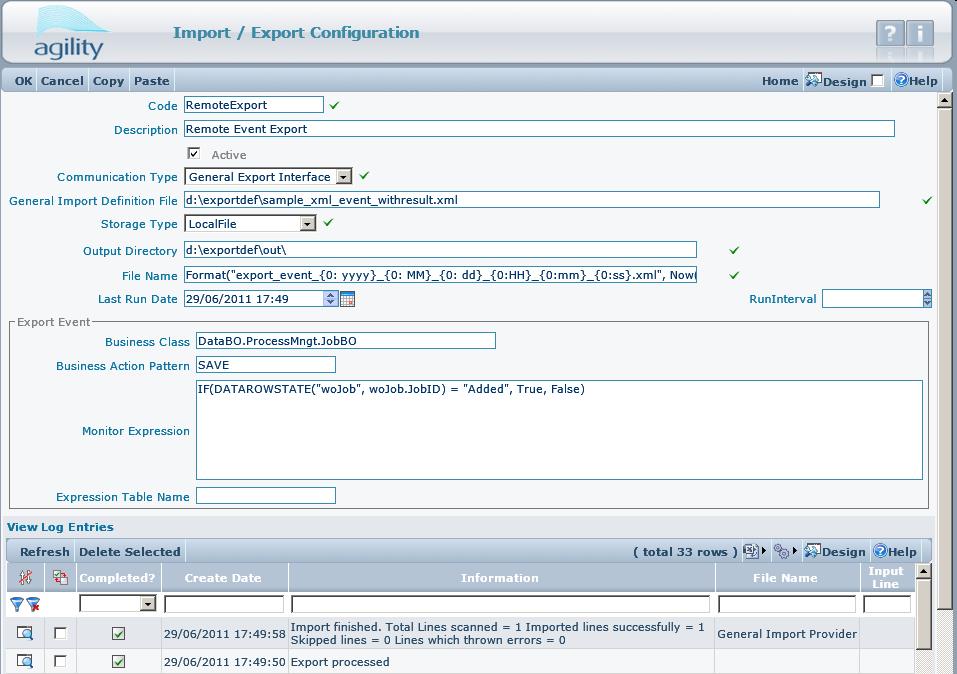
In this scenario, the most useful datacontext is called: externaldataset. This context has direct access to the Business Object which triggered the export event. You can find an example with externaldataset context usage in the file "sample_xml_event.xml".
Export to Remote Connection
Export to Remote Connection is not extra functionality of the export, but rather the flow of import/export features. It allows for:
- preparing export data (do export)
- passing data to remote host (build request)
- retrieve request result
- import retrieved result.
Remote Connection is an option for Storage Type of General Export.
For Remote Connection You must define also Connection Name. Connection describe link to host.
- Url: Host url. This is a string expression, which is evaluated just before create request to host. Some hosts may require putting login and password information inside the url. String expression will allow to do so:
"http://somehost.org/Service?login=" + syImpExpRemoteConnection.Login
- Auth Type: Authentication type definition. Allowed values:
- Auto (also NULL)
- If NetworkLogin is not specified then Agility will connect without credentials (authentication). If NetworkLogin is present then .NET will select appropriate Authentication Type according to remote service requirements. Possible Types are: Basic, Digest, NTLM, Negotiate.
- Windows
- Uses windows integrated authentication. Used are credentials from user on which agility service is running.
- Digest: Forces Digest auth.
- Basic: Forces Basic auth.
- BasicNoChallenge: Forces Basic auth with each request. This option should be used only when remote service is unable to work with "Challenge Pattern". Pre Authenticate should have no effect with this Auth type, but it is recommended that it is set to false.
- Pre Authenticate: It is boolean property which can be set to each request from agility to remote service. In general it controls if authentication credentials should be cached with subsequent requests. Unfortunately there is no clear explanation of behavior of this flag with different authentication types. Reversed Engineered Recommendation is to set this flag to true only with Digest or Basic auth.
- Login and Password: Helps to define internal web service credentials, you can put them in url and inside export body (will be explained further)
- NetworkLogin and NetworkPassword: Those parameters define credentials for web server authorization (BASIC, DIGEST,...). Available are all methods supported by asp.net framework.
- Domian: Allow to explicitly specify domain. Usually when remote service authentication relay on Domain it has defined default domain. In such case Domain can be skipped.
- Method: Http method GET or POST
- Retry Count: System will try RetryCount times to communicate with the host before giving up.
- Retry Delay: Sleep time between retries (in seconds)
- Soap Fault Retry Count: Number of system attempts to call remote service when service returns soap fault. It is used only when underlying respond import recognizes fault and throws validation error in mappings sections.
- Soap Fault Retry Delay: Sleep time between soap fault retries (in seconds). It is used only when underlying respond import recognizes fault and throws validation error in mappings sections.
When export is set up as "Remote Connection" then extra information, are available inside the export definition. As already mentioned, information available in Remote Connection Details, can be used to create export data. Data from Remote Connection Details can be accessed through string expression variables (globally available in any part of the export):
- #RemoteConnection.NetworkLogin
- #RemoteConnection.NetworkPassword
- #RemoteConnection.Login
- #RemoteConnection.Password
- #RemoteConnection.Code
- #RemoteConnection.Description
- #RemoteConnection.Type
- #RemoteConnection.Protocol
- #RemoteConnection.Url
For example one of method to login user with General Import Service is to create xml, which contains below element (anywhere in xml file):
"<LoginService xmlns=\"http://www.fastnetasp.com/GeneralImport\">
<login>" + #RemoteConnection.Login + "</login>
<password>"+ #RemoteConnection.Password + "</password>
</LoginService>"If the remote host returns useful information, the system can process it with the import routine. Definition of such an import should be embedded inside the export definition:
<export>
<contents>
...
</contents>
<import>
<mappings>
......
</import>
</export>There is no extra functionality which binds export data with import. Import is a separate process which has access only to the result generated by the web service. For example if You wish to export some jobs to a service, and after successful export update with information that the export is processed properly by service, then the Service result must carry information to identify the job to be updated with import data. Check examples for better understanding: -('export\sample_xml_event_withresult.xml' and 'import\import_wojob_def.xml').
Request Retry on Web exceptions
When system do request to remote system it is possible that remote system is not available or return exception "Soap Fault". In both cases it is WebException. When remote service is unavailable then Retry Count and Retry Delay is used (Remote Connection Definition). When remote service respond with Soap Fault then GI will always try to import this Fault. Import definition of respond not necessary must be aware of SoapFault. When handling of SoapFault is not defined in import then import will finish without error but with information that nothing was imported. In queue this respond will be marked as 'Fail'. In above situation no retry will be made to remote system. In some cases some Soap Error Types should cause Request Retry. It is possible with import definition. When validation in mappings section throws exception and respond is SoapFault then such Request is Repeated according to Soap Retry Count and Soap Retry Delay (Remote Connection Definition). Below diagram is representing flow of handling respond when WebException occurs. Each time when system will try to retry request it will update queue with MessageResult and will set status to Retry.
Export and Import Queue
Export and import make use of a Queue only when it comes to communicating over the http protocol (web services). The Queue is responsible for delivering http requests and retrieving results in background.
ImportExportQueue works in a similar way as GeneralInterfaceQueue. It uses the same app domain to handling queue. Queue information can be accessed through the menu: System Configuration->Import Export->Queue.
General Import
The General Import is extended with capabilities of working as web service.
Import definition extensions for web
The Web service communication relies on exchange of xml documents. Web services mostly operate with SOAP protocol. There is nothing special with handling SOAP protocol, it is purely an xml file, and the import handles it like any other xml file. It is up to the designer to create an import definition which can deal with SOAP structure. The advantage of handling import files at low level (level of soap protocol) is that we are not constrained to SOAP protocol. The system supports not only any kind of xml request, but also csv requests. The SOAP protocol is preferred, as it is well documented and supported by any platform.
The Import definition is extended with a section for defining the import result. This functionality is requirement for web services communication. To create result You must add resultexport section to import definition. Resultexport is basically General Export Definition, but additionally in context of Import it has access to imported data. Access to Imported data is made through export context type called mappings. Access for mappings data in resultexport looks exactly the same as for mapping in import. But in this case mappings are extended with some important information. Extended mapping information is accessible in the string expression with #Result prefix:
- Result.Key : data key of imported data
- Result.ImportMode : import mode (add / update)
- Result.IsOK : result info status flag
- Result.Message : result info message
- Result.BusinessAction : selected import business action
- Result.IsImported : row import status flag
Thanks to extended data placed in mappings, string expression is executed in context of already created/updated data by import. In other words you can access data in string expression from mappings: #Import.JobDescription and from agility woJob.JobCode
Import configuration
Import configuration options are available in the "interface/GeneralImport" section of agility configuration xml file.
<GeneralImport
ImportWebServiceEnabled="true"
DefaultUser="admin"
DefaultUserPass="admin"
WebServiceLocation="http://ursus/Agility35Demo/Services/GeneralImport.ashx"
/>- ImportWebServiceEnabled: it is general switch for import web service functionality.
- DefaultUser, DefaultUserPass: default user credentials used when request doesn't have credentials defined (explained in next chapter).
- WebServiceLocation: This url has minor meaning for import. It is used for publishing wsdl definition with proper default url of web service.
- ADIntegration: If set to true then user authorization is based on Agility Active Directory Integration Configuretion (include role based integration).
Logging to system
Login to agility with import service is possible in several ways (all possible ways). System tries to retrieve user credentials from request or import data. If user credentials are not present system will use default credentials defined in config file. Left blank default user credentials enforces login from request. You can pass user credential through url:
http://.../Services/GeneralImport.ashx/LoginService?GeneralImportUserName=admin& GeneralImportUserpass=adminPut user credentials inside imported xml data:
<LoginService xmlns="http://www.fastnetasp.com/GeneralImport">
<login>john</login>
<password>doe</password>
</LoginService>You can put above piece of xml in any part of import xml data. If web service client is smart enough than it can login through exposed in import service LoginService method, process import files in session, and finally call LogoffService.
Definitions of LoginService and LogoffService methods are available under url:
http://.../Services/GeneralImport.ashx?wsdlBinding Import Data request with import definition
The Import service expect requests with data to import. The Request must carry information about which Import Definition (defined in agility) should process the incoming request data.
Database import definition is extended with the unique code field. This field defines the name of the method exposed in the service. It is possible to select the appropriate import definition by the url path:
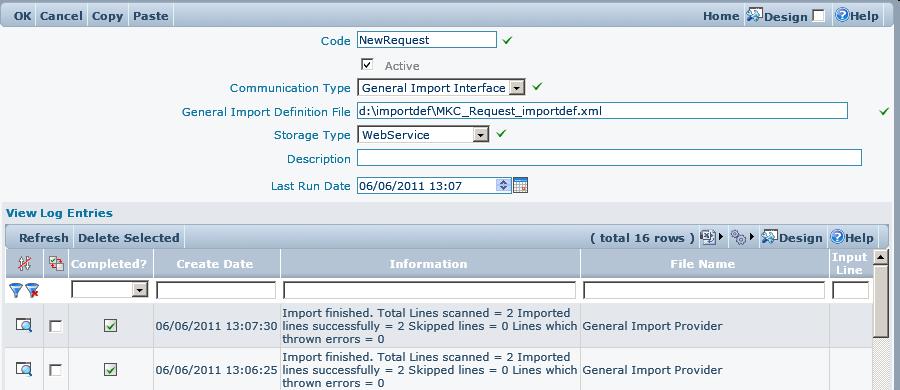
http://.../Services/GeneralImport.ashx/'''NewRequest'''?otherparameter=somethingThere are other native SOAP ways to define the requested method, unfortunately it different in version 1.1 and 1.2 (of soap protocol). Both versions are supported by Import Service: • SOAP1.1 requires an additional header in the request:
SOAPAction: http://www.fastnetasp.com/GeneralImport/'''NewRequest''';• With SOAP 1.2 protocol Import Service will use the name of the first child element inside the SOAP body:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<soap12:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap12="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope">
<soap12:Body>
< '''NewRequest''' xmlns="http://www.fastnetasp.com/GeneralInterface">
....
</ '''NewRequest''' >
</soap12:Body>
</soap12:Envelope>Warning! Url Path supersedes the SOAP method selection.
What else is there?
- WSDL Web Service Definition Language. This language is very helpful for developers when they need to reference some published over the web service methods. With wsdl most programming platforms can create proxy with translated to objects, parameters and results. For now wsdl definition is static and define only two embedded into import service methods: LoginService, LogoffService. If you wish to extend wsdl, you can do it manually by modification GeneralImportWsdl.xml file. This file is available in same path as GeneralImport.ashx. To access wsdl definition (add web reference in client application) use url:
http://.../Services/GeneralImport.ashx?wsdl- Generic SOAP exceptions. When data is passed to import procedure then Import Definition itself can create result with failed information (not necessarily SOAP fault) . But in case when error appears earlier, or something goes wrong with import system will always produce generic SOAP Fault. Soap fault is generated with different fault codes, which can be accessed by client application for further actions. Possible fault codes with Import Service:
- ServiceDisabled
- LoginFault
- LogoutFault
- RequestDefinitionFault
- ProcessingFault
- Queue and log. All request data and results are stored in ImportExportQueue:
System Confiquration - > Import Export -> Queue.
Import log place doesn't change. It is available in import export definition form details.
Exchange data with localization
There is a potential problem with data exchange when import and export works on machines with different cultures. By default all conversions are made with culture of running application. |The only safe way to get a portable format is to operate on invariant cultures. There are already capabilities embedded into string expression functions which allow conversion of data from and to an invariant culture.
ToInvariantStr(value)
FromInvariantStr(type, value)ToInvariantStr function should be always used with export to convert values into string. Opposite function FromInvariantStr should be used on import side. FromInvariantStr has additional type parameter which determine type of returned value conversion. Recoginized are 3 types "int", "decimal", "datetime". There is additional convert function which is capable to convert data in desired culture. It can be used as replacement for ToInvariantStr, FromInvariantStr functions.
Convert(type, value, culture)Type is a string with desired destination type ["decimal", "string", "int", datetime"].
Culture is a string which represents culture notation for conversion ["en-GB", "en-US", "pl-PL"]. Full list of allowed names can be found under url:
http://www.csharp-examples.net/culture-names/
Invariant culture is represented by empty string: "". Culture parameter can be skipped, in such case current culture will be used. Convert function result is conversion of Value according desired to type and culture.
Examples:
ToInvarintStr(inItem.price)
FromInvariantStr("decimal", #Import.price)
Convert("decimal", #Import.price, "en-GB")New Features (Version7.1)
String expression templates
Templates add-on for string expressions is mechanism which allows to create XML and HTML documents in more natural way. Quick example:
<foreach table="woJob" datacontext="database" classname="DataBO.ProcessMngt.JobBO">
<dbfilter>MAXRESULTS 10</dbfilter>
<data type="template-xml">
<woJob ID="{woJob.JobID}">
<JobCode>{woJob.JobCode}</JobCode>
<Description>{woJob.FullDescription}</Description>
</woJob>
</data>Equivalent export without templates:
<foreach table="woJob" datacontext="database" classname="DataBO.ProcessMngt.JobBO">
<dbfilter>MAXRESULTS 10</dbfilter>
<data>
<![CDATA[
"<woJob ID=\"" + XmlEncode(woJob.JobID) + "\">
<JobCode>" + XmlEncode(woJob.JobCode) + "</JobCode>
<Description>" + XmlEncode(woJob.FullDescription) + "</Description>
</woJob>
"
]]>
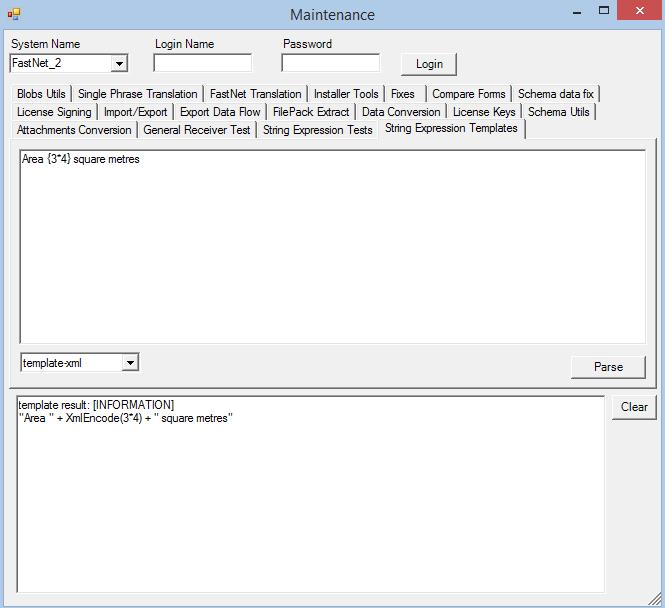
</data>Any string expression element in export (data, const, variable) can use templates. Template is not another language similar to string expression it is more likely string expression extended with macros. When using templates string expression must be placed in {} brackets. Text outside brackets is merged with string expression evaluation result. Internally template is transformed to string expression and executed as standard string expression.
Template:
- Area {3*4} square metres
Is translated to:
- "Area " + 3*4 + " square metres"
Using templates in xml or html export is more natural as xml structure is embedded directly in export structure. Basic xml validation embedded in agility will check if xml structure is ok during save of definition. It allows to catch hard to find typo bugs without need to run export. As side effect of templates develop Maintenance is extended with tool for translating macro to equivalent string expression. It can be handy for extending or debugging templates.
Currently there are defined three types of templates:
- template-raw ["Area " + 3*4 + " square metres"]
- template-html ["Area " + HtmlEncode(3*4) + " square metres"]
- template-xml ["Area " + XmlEncode(3*4) + " square metres"]
- stringexpression
Only difference with templates raw/html/xml is encoding of string expression result. Raw does not encode string expression. When type is set to “stringexpression” then template engine is not used and standard string expression must be used.
In export template is declared in type attribute:
<data type="template-xml">...
<const type="template-xml">...
<variable type="template-xml">...By default templates are not used but it is possible to set default template for whole export definition. When attribute defaulttype is set in contents element then all string expression elements will use default template without need to specify type in each element. Even if defaulttype attribute is set it is possible to override particular section with other template type.
<export><contents defaulttype="template-html">...String expression macros
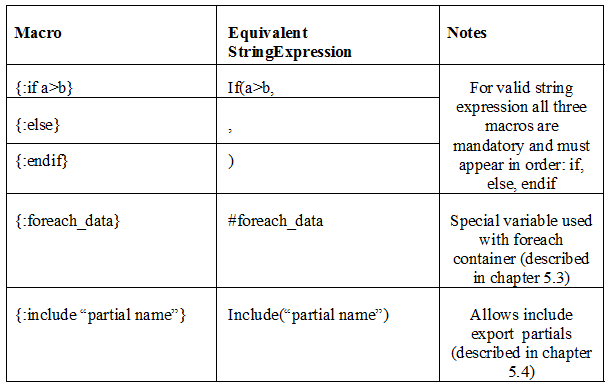
Currently macros are very limited and hardcoded. They can be used only along with templates. It should be easy to extend export with custom macros but it seems that custom macros feature is not something which can improve overall export structure. In general macro is something which replaces one piece of string with another.
Simple example of if/else/endif macros:
<data type="template-html">
Labour {emLabour.LabourFirstName} is
{:if emLabour.Suspended}
suspended
{:else}
available
{:endif}
</data>Simmilar as wih templates macro is translated to equivalent string expression.
Foreach container
Foreach element can be extended within container. Very often in export we fall into situation that some element should be available in export data but only when data which describe it contains any records. Container idea is to define element inside foreach which will be evaluated only when there was any data matched. Example:
<foreach table="woJob" context="data" dataclass="">
<dbfilter>woJob.StartDate >= DATEADD(NOW(), 'DAY', -1)</dbfilter>
<container>
<JobsList>{:foreach_data}</JobsList>
</container>
<data>
<Job ID={woJob.JobID}>
{woJob.JobCode}
</Job>
</data>
</foreach>In above example if there are any jobs matched by filter, then export result will look like:
<JobList>
<Job ID="123">110003</Job>
<Job ID="124">110004</Job>
</JobList>If there are no matched results then export will not output any structure (empty string). Without foreach container it was very difficult to solve similar problems.
Export partials
Export partials allows do define export sections which can be used (included) multiple times in export. With partial it is possible to create recurrences. Export with partial example:
<export>
<contents defaulttype="template-html">
<partial name='submenu'>
<foreach table="upMenuLine">
<filter><sort>Order</sort></filter>
<container>
<ul>{:foreach_data}</ul>
</container>
<data>
<li>
{upMenuLine.Caption}
{:include "submenu"}
</li>
</data>
</foreach>
</partial>
<foreach table="upMenu" datacontext="dataset" classname="DataBO.UserProfile.MenuBO">
<dbfilter>upUser.UserID = #UserID</dbfilter>
<data>{:include "submenu"}</data>
</foreach>
</contents>
</export>Partial structure is created and evaluated during export runtime with include macro or function. Partial will inherit parent context. It means that the same partial evaluation depends on context it is executed. It also means that partial not require full context definition (classname, datacontext) as it is inherited from caller.
Examples
Import
In
Out
Export
Out
-
file:///C:/Users/Aleksandra/Desktop/Dokumentacja%20-%20praca/examples/export/out/export.html]
-